

|
|
Tweet |

![]()
| An old-style cup-and-cone bottom bracket. The lockring wrench is about to loosen the lockring, the pin wrench is engaging two of the holes in the adjustable cup | 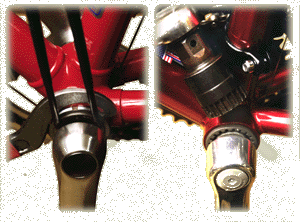 |
A cartridge bottom bracket. The splined tool is shown above the bottom bracket. The crank would need to be removed to actually use the tool. Information on servicing cartridge bottom brackets |
|---|
This article deals with the older type of bottom bracket, which consists of:
![]()
![]()
Do not think that you don't need a bottom bracket sleeve just because you have a closed seatpost! Although open seatposts on bikes without mudguards are the leading cause of dirty bottom brackets, even the cleanest, most carefully made bike is likely to have leftover brazing flux, paint chips, or other debris inside its frame tubes. All of this will eventually wind up in your bottom bracket, thanks to the modern miracle of universal gravitation!
Most newer bicycles come with "caged" bearing balls-the balls are held in a metal or plastic retainer. This makes it easier to install the balls, but usually at a cost in performance. A standard three-piece type bottom bracket takes 11 loose 1/4-inch balls per side. Most retainers hold fewer balls, so each ball and its contact points with the cup and cone are more heavily stressed. This causes higher friction and more rapid wear.
If your bottom bracket came with retainers holding fewer than 11 balls, I strongly recommend that you replace them with loose balls. This is not really difficult to do. if you know how.
The frame should be lying on its right side, with the fixed cup and liner installed. Squirt plenty of grease into both cups.
Set 11 balls into the adjustable (left) cup. Drop the shorter end of the spindle into the cup, and it will hold the balls in place even if you are using a thin grease. Holding the adjustable cup and spindle as a unit, turn them over so that the cup is on top. Set this assembly aside in this position, supported by the spindle. (A convenient place to put it temporarily is into the right crank: the chain wheel will prevent it from falling over.)
Next, stick a finger up through the hole in the fixed cup to keep the balls from falling through. Drop 11 balls down into the cup and arrange them in a circle around your finger.
Then, pick up the spindle (with the adjustable cup already installed) and lower it down until it rests on the finger that is sticking up through the fixed cup. Lower it farther, until you can begin to screw the adjustable cup into the bottom bracket threads.
Keep the spindle supported from below until the adjustable cup is screwed well in, because if you release the spindle while the cup is very loose, the balls may fall out of position.
![]()
![]()
Adjusting the tightness of bottom bracket bearings is similar to adjusting wheel bearings, but slightly more complicated. With wheel bearing cones, tightening the locknut presses on the cone, so that the bearing adjustment becomes slightly tighter than it was before you tightened the locknut. But when you tighten the lockring on the adjustable cup of a conventional bottom bracket. the bearing adjustment will sometimes become tighter, sometimes looser!
As the locknut pushes against the edge of the bottom bracket shell, it pulls the adjustable cup outward just a little bit. When this is all that happens, the bearing gets looser. But sometimes, as you tighten the lock ring, the friction of the threads will cause the adjustable cup to turn with the lockring--in this case, the adjustment will become tighter. You cannot tell which way it will go on a particular bicycle until you try it.
For this reason, it is a waste of time to try to judge the adjustment of a bottom bracket bearing until the lockring has been securely tightened. If you are adjusting a bottom bracket that is tending to rotate the cup with the lockring, you may be tempted to hold the cup stationary with your pin tool -- this is not a good idea, because it can put excessive stress on the pins of the pin tool. It is better in such cases to allow the cup to rotate and make use of a little "Kentucky windage."
In cases where the cup tends to turn with the lock ring, the bearing adjustment will become tighter when the lockring is tightened securely. If it becomes too tight, loosen the lock ring and cup together, then turn the lockring clockwise on the cup, then re tighten the lockring and cup as a unit until secure. Recheck the bearing adjustment. If it is still too tight, repeat this procedure. If it is too loose, loosen both pieces together, turn the lock ring just a bit counterclockwise, and re tighten both pieces together.
If, on the other hand, the lockring of the bicycle you are working on can be tightened without tending to turn the adjustable cup, you must first adjust the cup so that the bearings are too tight, then tighten the lockring. The lockring will pull the adjustable cup out just a bit, and if you have judged correctly, the bearing will then be correctly adjusted.
Take your time and be patient. As you approach the ideal adjustment, the corrections will need to be made just a couple of degrees at a time.
Judging the adjustment is basically the same as with wheel bearings -- perfection consists in having no play and no friction. Perfection is, of course, impossible in this vale of tears, so the best you can do is to minimize both.
The bottom bracket is much more heavily stressed than the wheel bearings, and you will not usually be able to make it feel nearly as perfect as you can with a good wheel bearing. The adjustment should be made with the cranks off the spindle.
I like to pretend to be a yegg turning the knob of a safe, trying to feel the tumblers drop in. Turn it for several complete revolutions in both directions. It should not have any roughness or unevenness at any point. If it does, it is a sign that the spindle, cups, or balls are damaged, or that there is dirt in the bearing.
Make a mental note of how easily the spindle turns when the bearing is too loose-it should turn just as freely when you have finished adjusting it.
Bearing play is checked by trying to rock the end of the spindle up and down. Ideally, there should be no play at all, but in almost all cases, if you eliminate the play completely, the bearing will bind. If in doubt, it is better to have the bearing just a bit too loose than too tight [But see Jobst Brandt's opinion, which is opposite -- John Allen]. In my experience, only Campagnolo bottom brackets can be adjusted for no play and still turn as freely as they should.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Last Updated: by John Allen