
|

| Tyre Sizing Charts: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inch Based Systems: | Metric Based Sizing Systems: | ||
| Decimal | Fractional | French | ISO/E.T.R.T.O. |

|

| Tyre Sizing Charts: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inch Based Systems: | Metric Based Sizing Systems: | ||
| Decimal | Fractional | French | ISO/E.T.R.T.O. |
![]()
This article is also available in American English!
For more general tyre information, see my tyres article.
Bicycle tyres come in a bewildering variety of sizes. To make matters worse, in the early days of cycling, every country that manufactured bicycles developed its own system of marking the sizes. The same size tyre would be known by different numbers in different countries. Even worse, different-sized tyrea that were not interchangeable with one another were often marked with the same numbers!
This page covers sizes in common use as of its writing, and a number of older sizes. Sutherland's Handbook for Bicycle Mechanics, 3rd through 6th edition, covers dozens of additional, antique sizes. The 6th edition is available on CD ROM from Sutherland's. Better bike shops have a copy.
![]()
![]()
To determine which tyre size will fit, perform measurements on the bicycle's fork and frame.
If the bicycle has rim brakes, the rim must line up with the brake shoes and so only one rim size or a small range of sizes will work. So, first measure the distance from where the center of the hub axle would be in a dropout to the center of a brake shoe. Then look up the rim radius in the ISO table on this page. A different rim size may be possible with different brakes, though longer brake reach generally results in poorer brake performance.
The front tyre must not reach the fork crown; the rear tyre must not reach the seatstay bridge or chainstay bridge. Take measurements from the axle position to the fork crown, chainstay bridge and seatstay bridge. Tyre outside radius is nominally the rim radius plus the tyre width, and as much as 1 cm greater for a tyre with a deep tread. A tyre must have typically 1 cm clearance, 2 cm if a fender will be installed, but do not use a wheel that is much smaller, or a pedal is too likely to strike the ground in cornering. On a bicycle with horizontal dropouts, additional clearance to the chainstay bridge is desirable so the wheel can be removed without deflating the tyre.
The space between the fork blades or stays must be wide enough to clear the tyre, with a few mm extra on each side in case the wheel goes slightly out of true. Measure at the radius of the widest part of the tyre, usually the rim radius plus half the tyre width --except that the widest part may be at the tread of an off-road tyre. Nominal tyre width is marked on the tyre; actual width can be measured if the tyre is installed on a rim.
If the bicycle has hub brakes (drum, disk, coaster), different rim sizes are possible as long as the tyre is fits the frame. A larger rim goes with a skinnier tyre, and vice versa..
The traditional sizing systems are based on a measurement of the outside diameter of a tyre. This would usually be measured in inches (26", 27", etc.) or millimeters (650, 700, etc.).
Unfortunately, evolution of tyres and rims has made these measurements lose contact with reality. Here's how it works: Let's start with the 26 x 2.125 size that became popular on heavyweight "balloon tyre" bikes in the late '30's and still remains common on "beach cruiser" bikes. This size tyre is very close to 26 inches in actual diameter. Some riders, however were dissatisfied with these tyres, and wanted something a bit lighter and faster. The industry responded by making "middleweight" tyres, marked 26 x 1.75 to fit the same rims. Although they are still called "26 inch", these tyres are actually 25 5/8", not 26". This same rim size was adopted by the early pioneers of west-coast "klunkers", and became the standard for mountain bikes. Due to the appetite of the market, you can get tyres as narrow as 25 mm to fit these rims, so you wind up with a "26 inch" tyre that is more like 24 7/8" in actual diameter! And fatbike tires as wide as 5 inches!
A second number or letter code would indicate the width of the tyre. (26 x 1.75, 27 x 1 1/4...650B, 700C...)
Inch-based designations sometimes express the width in a decimal (26 x 1.75) and sometimes as a common fraction (26 x 1 3/4). This is the most common cause of mismatches. Although these size designations are mathematically equal, they refer to different size tyres, which are NOT interchangeable. It is dangerous to generalize when talking about tyre sizing, but I would confidently state the following:
Competitive pressures have often led to inaccuracy in width measurement. Here's how it works: Suppose you are in the market for a high performance 700 x 25 tyre; you might reasonably investigate catalogues and advertisements to try to find the lightest 700-25 available. If the Pepsi Tyre Company and the Coke Tyre Company had tyres of equal quality and technology, but the Pepsi 700-25 was actually a 700-24 marked as a 25, the Pepsi tyre would be lighter than the accurately-marked Coke 700-25. This would put them at a competitive advantage. In self defense, Coke would retaliate by marketing an even lighter 700-23 labeled as a 700-25.
This scenario prevailed throughout the '70's and '80's. The situation got so out-of-hand that cooler heads have prevailed, and there is a strong (but not universal) trend toward accurate width measurements.
Some road bicycles have extremely tight clearances and will not fit an honest 28mm tyre. See comments in our article on fenders.
![]()
![]()
 The ISO (E.T.R.T.O.) System:
The ISO (E.T.R.T.O.) System:ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, has developed a universal tyre and rim sizing system that eliminates this confusion. (This system was formerly known as the "E.T.R.T.O." system, developed by the European Tyre and Rim Technical Organisation.)
The ISO system uses two numbers. The first is width in millimeters. For the rim, this is the inner width between the flanges, as shown in the diagram; for the tyre, it is the inflated width. This will vary a bit depending on the width of the rim.
The second ISO number is the critical one: it is the diameter of the bead seat of the rim, in mm ("B.S.D."). Generally, if this number matches, the tyre involved will fit onto the rim; if it doesn't match, the tyre won't fit.
For example, a 700 x 20 C road tyre would be a 20-622; a 700 x 38 hybrid tyre would be a 38-622. The width difference between these sizes would make them less-than ideal replacements for one another, but any rim that could fit one of them would work after a fashion with the other.
A general guideline is that the tyre width should be between 1.45/2.0 x the inner rim width.
If you flatten out a tyre and measure the total width from bead to bead, it should be approximately 2.5 x the ISO width.
If your tyre is too narrow for the rim there's an increased risk of tyre/rim damage from road hazards.
If its too wide for the rim, there's an increase risk of sidewall wear, and a greater risk of loss of control in the event of a sudden flat.
The tables below give a partial listing of traditional tyre sizes, with their ISO bead-seat equivalents. The ISO comparison list at the bottom of this page covers all sizes which we know to be in production as of 2016. The fractional, decimal and French lists cover common sizes.
| Fractional | ISO | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 36 inch | 787 mm | Unicycles, some novelty bicycles |
| 32 inch | 686 mm | Unicycles, some novelty bicycles |
| 29 inch | 622 mm | This is a marketing term for wide 622 mm ("700C") tires. |
| 28 x 1 1/2 | 635 mm | English, Dutch, Chinese, Indian Rod-brake roadsters (Also marked F10, F25, 700 B) |
| 622 mm | (F.13) Rare Canadian designation | |
| 28 x 1 5/8 x 1 1/2 |
Northern European designation for the 622 mm (700 C) size | |
| 635 mm | Old Swedish designation | |
| 27 x anything except "27 five" and 609 mm Danish | 630 mm | Older road bikes. |
| 27 x 1 1/2 | 609 mm | Rare Danish size |
| 26 x 1 (650 C) |
571 mm | Triathlon, time trial, small road bikes. Old Schwinn S-4 |
| 26 x 1 1/4 | 597 mm | Older British sport & club bikes |
| 26 x 1 3/8 (S-6) |
Schwinn "lightweights" | |
| 26 x 1 3/8 (E.A.3) | 590 mm | Most English 3-speeds, department-store or juvenile 10 speeds |
| 26 x 1 1/2 (650B) | 584 mm | French utility, tandem and loaded-touring bikes, a very few Raleigh (U.S.) & Schwinn mountain bikes. |
| 26 x 1 3/4 (S-7) |
571 mm | Schwinn "middleweight" cruisers |
| 26 x 1, 1 1/8 | High performance wheels for smaller riders, common on Cannondale bicycles | |
| 24 x 1, 1 1/8, 1 3/8 | 520 mm | High performance wheels for smaller riders, BMX; Terry front |
| 24 x 1 1/8 | 520 mm or 540 mm! |
Caveat emptor. 540mm is common on wheelchairs. |
| 24 x 1 1/4 | 547 mm | British or Schwinn Juvenile |
| 24 x 1 3/8 (S-5) |
Schwinn Juvenile lightweights | |
| 24 x 1 3/4 (S-7) |
520 mm | Schwinn "Middleweights" |
| 24 x 1 3/8 (E-5) |
540 mm | British Juvenile, most wheelchairs; common on women's utility bicycles in Japan. |
| 22 x 1 3/8 NL | 489 mm | Dutch juvenile |
| 20 x 1 1/8 20 x 1 1/4 20 x 1 3/8 |
451 mm | Juvenile lightweights, BMX for light riders, some recumbents, some folding bicycles |
| 20 x 1 3/4 | 419 mm | Schwinn juvenile |
| 20 x 2 | 438 mm | Swedish |
18 x 1 3/8 |
400 mm | British juvenile. 18 x 1 is used on "micro" and smaller BMX bicycles |
| 17 x 1 1/4 | 369 mm | Alex Moulton AM series |
| 16 x 1 3/8 | 349 mm | Older Moulton; Brompton & other folders, recumbent front, juvenile |
| 16 x 1 3/8 | 337 mm | Mystery tire |
| 16 x 1 3/8 | 335 mm | Polish juvenile |
| 16 x 1 3/4 | 317 mm | Schwinn Juvenile |
| 14 x 1 3/8 | 298 mm | Moulton mini, etc. |
| 12 1/2 x anything | 203 mm | Juvenile, scooters |
| 10 x 2 | 152 mm | Wheelchair caster |
| 8 x 1 1/4 | 137 mm | Wheelchair caster |
![]()
![]()
| Decimal | ISO | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 29 inch | 622 mm | This is a marketing term for wide 622 mm ("700C") tires. |
| 28 x decimal | Some German tire companies use this non-standard designation for 622 mm ("700C") tires -- violates Brown's law! | |
| "27 five" (meaning 27.5) | 584 mm | Marketing term for wide, knobby 584 mm tires. Some Mountain bikes |
| 26 x 1.00 through 5.0 | 559 mm | Most Mountain bikes, cruisers, fatbikes etc. Old Schwinn designation was S-2 |
| 26 x 1.25 (rare) | 599 mm | Very old U.S. lightweights |
| 26 x 1.375 (rare) | Very old U.S. lightweights | |
| 24 x 1.,5 (Dutch, rare) | 534 mm | Still made in India as of 2022 |
| 24 x 1.5-24 x 2.125 | 507 mm | Juvenile mountain bikes, cruisers |
| 22 x 1.75, 22 x 2.125, 2.1 2.3, 2.4 | 457 mm | Juvenile; BMX "cruiser" category (over 22 1/2" OD), street, freestyle for adult riders |
| OS 20 x 1.6, OS 20 x 1.75, OS 20 x 1.85 |
451 mm | Adult-size BMX racers. Under 22 1/2" OD to fit into "class" category. |
| 20 x 1.5-20 x 2.125 | 406 mm | Most BMX, juvenile, folders, trailers, some recumbents |
| 18 x 1.5 | 355 mm | Birdy folding bikes |
| 18 x 1.75-18 x 2.125 | Juvenile | |
| 16 x 1.75-16 x 2.125 | 305 mm | Juvenile, folders, trailers, Strida, early DaHon, some recumbents |
| 14 x 1.75-14 x 2.125 | 254 mm | Juvenile |
| 12 1/2 x anything | 203 mm | Juvenile, scooters |
In the French system, the first number is the nominal outside diameter in mm, followed by a letter code for the width: "A" is narrow, "D" is wide. The letter codes no longer correspond to the tyre width, since narrow tyres are often made for rim sizes that originally took wide tyres; for example, 700 C was originally a wide size, but now is available in very narrow widths, with actual outside diameters as small as 660 mm.
![]()
| French Size | ISO | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 700 A | 642 mm | Obsolete |
| 700 B | 635 mm | Rod-brake roadsters. |
| 700 C | 622 mm | Road bikes, hybrids, "29 inch" MTBs. (28 x 1 1/2 F.13 Canada) |
| 700 D | 583 mm | Oddball size formerly used on some GT models. Often incorrectly reported as 587 mm. 650B tyre (584 mm) is close enough. |
| 650 A | 590 mm | French version of 26 x 1 3/8; Italian high-performance bikes for smaller riders |
| 650 B | 584 mm | French utility bikes, tandems, and loaded-touring bikes; some older Raleigh and Schwinn mountain bikes. Also called 27 five. We have a page about this size. |
| 650 C | 571 mm | Triathlon, time trial, high performance road bikes for smaller riders |
| 600 A | 541 mm | European Juvenile road bikes, most wheelchairs |
| 550 A | 490 mm | European Juvenile road bikes |
| 500 A | 440 mm | European Juvenile, folding |
| 450 A | 390 mm | European Juvenile |
| 400 A | 340 mm | European Juvenile |
| 350 A | 288 mm | European juvenile |
![]()
![]()
| Bead Seat Diameter, mm | Bead Seat Radius, mm | Traditional Designations |
|---|---|---|
| 787 | 393.5 | 36 inch |
| 686 | 343 | 32 inch |
| 642 | 321 | 700A |
| 635 | 317.5 | 28 x 1 1/2, 700 B, 28 x 1 5/8 x 1 1/2 (old, Sweden) |
| 630 | 315 | 27 x anything except "27 five" and 609 mm |
| 622 | 311 | 700 C, 28 x 1 5/8 x 1 1/2 and other pairs of numbers, (but also see 635), 29 inch, 28 x 1 1/2 F.13 Canada |
| 609 | 304.5 | Rare Danish size, 27 x 1 1/2 |
| 599 | 299.5 | 26 x 1.25, x 1.375 -- old US size |
| 597 | 298.5 | 26 x 1 1/4, 26 x 1 3/8 (S-6) |
| 590 | 295 | 26 x 1 3/8 (E.A.3), 650 A |
| 584 | 292 | 650B, 26 x 1 1/2, "27 five" |
| 583 | 291.5 | 700 D -- oddball size made by GT |
| 571 | 285.5 | 26 x 1, 26 x 1 3/4, 650 C |
| 559 | 279.5 | 26 x 1.00- x 2.125, also fatbike tires up to 5 inches wide |
| 547 | 273.5 | 24 x 1 1/4, 24 x 1 3/8 (S-5) |
| 541 | 270.5 | 600 A |
| 540 | 270 | 24 x 1 1/8, 24 x 1 3/8 (E.5), |
| 534 | 267 | Dutch 24 x 1.5 |
| 520 | 260 | 24 x 1, 24 x 1 1/8, 24 x 1 3/8, 24 x 1 3/4 |
| 507 | 253.5 | 24 x 1.5- x 2.125 |
| 501 | 250.5 | British, 22 x 1 3/8, 22 x 1.00 |
| 490 | 245 | 550 A |
| 489 | 244.5 | Dutch juvenile 22 x 1 1/8 NL, 22 x 1 3/8 NL |
| 484 | 242 | 550 B |
| 457 | 228.5 | 22 x 1.75; x 2.1, x 2.125, x 2.3, x 2.4 |
| 451 | 225.5 | 20 x 1 1/8; x 1 1/4; x 1 3/8; OS20 x 1.6, 1.75, 1.85 |
| 440 | 220 | 500 A |
| 400 | 200 | 18 x 1 3/8, 18 x 1 |
| 438 | 219 | Dutch juvenile, 20 x 1 3/8 NL |
| 428 | 214 | Swedish, 20 x 2 |
| 419 | 209.5 | 20 x 1 3/4 Schwinn Juven |
| 406 | 203 | 20 x 1.5- x 2.125 |
| 400 | 200 | 18 x 1 |
| 390 | 195 | 450 A |
| 369 | 184.5 | 17 x 1 1/4 |
| 355 | 177.5 | 18 x 1.5- x 2.125 |
| 349 | 174.5 | 16 x 1 3/8 |
| 340 | 170 | 400 A |
| 337 | 168.5 | 16 x 1 3/8 |
| 335 | 167.5 | 16x 1 3/8 Polih juvenile |
| 317 | 158.5 | 16 x 1 3/4 |
| 305 | 152.5 | 16 x 1.75- x 2.125 |
| 298 | 149 | 14 x 1 3/8, Moulton Mini |
| 288 | 144 | 350 A |
| 254 | 127 | 14 x 1.75 |
| 252(?) | 126.5 | 12 x 1/5/8 (France). 254 will work - build up rim with tape. |
| 203 | 101.5 | 12 1/2 X anything. |
| 152 | 76 | 10 x 2 |
| 137 | 68.5 | 8 x 1 1/4 |
![]()
![]()
Although you can use practically any tyre/rim combination that shares the same bead seat diameter, it is unwise to use widely disparate sizes.
If you use a very narrow tyre on a wide rim, you risk pinch flats and rim damage from road hazards.
If you use a very wide tyre on a narrow rim, you risk sidewall or rim failure. This combination causes very sloppy handling at low speeds. Unfortunately, current mountain-bike fashion pushes the edge of this. In the interest of weight saving, most current mountain bikes have excessively narrow rims. Such narrow rims work very poorly with wide tyres, unless the tyres are overinflated...but that defeats the purpose of wide tyres, and puts undue stress on the tyre fabric and rim sidewalls.
The "fatbike" phenomenon has led to the availability of very wide tyres and rims. These should only be used together.
Georg Boeger has kindly provided a chart showing recommended width combinations:
| Which tyre fits safely on which rim? [all dimensions in millimeters] |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tyre width | ||||||||||||||
| Rim width (interior) |
18 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 28 | 32 | 35 | 37 | 40 | 44 | 47 | 50 | 54 | 57 |
| 13 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| 15 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| 17 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
| 19 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 21 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| 23 | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| 25 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
The cross-section of a tyre's fabric is an arc of a circle -- only a full circle with tubulars. The rim takes up the part of the circle that is not represented by the tyre.
The rim is typically 0.7 times as wide as the tyre, and a bit of trigonometry will get you that the rim occupies about 90 degrees of what would be the circumference of the circle. The tyre occupies the other 270 degrees (3/4 of the circle) and so the width when mounted on the rim is 4/(3 * pi), about 0.4, times the width when laid out flat.
Rim and tyre widths of course vary, so this result is not exact.
A suggestion to measure tyre width with the tyre laid out flat first appeared in the third edition of Sutherland's Handbook for Bicycle Mechanics (1980), and I was the author of that suggestion.
That edition also included the first published tyre-size chart using the ETRTO marking standard, other than in the original ETRTO technical document. I performed the calculations for the chart on a Hewlett-Packard Model 27 pocket calculator.
--John Allen
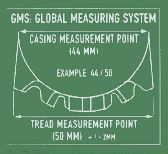 GMS Global Measuring System: The current industry standard for specifying the actual inflated size of a bicycle tyre does not account for subtle variation in tread and casing size. To address this problem and provide you with more information for comparing tyres, WTB has introduced the Global Measuring System (GMS) for tyre measurement.
GMS Global Measuring System: The current industry standard for specifying the actual inflated size of a bicycle tyre does not account for subtle variation in tread and casing size. To address this problem and provide you with more information for comparing tyres, WTB has introduced the Global Measuring System (GMS) for tyre measurement.
The GMS uses a two-number system: the first number is the width of the casing, and the second number is the width of the tread, both in millimeters. These measurements are taken on a rim which is 20 mm wide at the bead-capturing point, with a tyre inflated to 60psi and maintained for 24 hours.
In addition to being able to accurately size a tyre, knowing the actual casing size and tread width provides an indication of air volume, tread characteristics and tread contact area; all of which provide you with a more concise idea of what ride characteristics to expect from each of WTB's tyres.
![]()
Tubular tyres are mainly used for racing. A tubular tyre has no beads; instead, the two edges of the carcass are sewn together (hence the term "sew-up") with the inner tube inside. Tubulars fit only on special rims, where they are held on by cement.
Unless special cement which does not allow on-road replacement of a tyre is used, tubulars "squirm" against the rims and are slower than the best wired-on tyres, even though lighter -- see details from Jobst Brandt.
Tubulars existed in several different sizes, but only 700c and 26-inch tubulars are readily available these days. Beware: sizes of 26" and 24" tubulars are not well-standardized. Take the rim with you when buying a tyre, and vice versa. Size variations of tubulars are covered in Sutherland's Handbook for Bicycle Mechanics, 7th Edition, available from Sutherland's, and on the mechanic's bookshelf at better bike shops.
In clincher tyres, there is a real difference between "700c" and "27 inch" sizes, but for tubulars this is a false distinction. Whenever you see mention of "27 inch tubulars" the writer is actually referring to standard full-sized tubulars, as used on most racing bikes.
If you want to sound like an ignorant yahoo, call them "tubies" or "tubeless tyres." Tubeless tyres for bicycles have bead wires, and are special only in being designed to hold air without an inner tube.
![]()
![]()
If you would like to make a link or bookmark to this page, the URL is:
https://www.sheldonbrown.com/tyre-sizing.html
Last Updated:
by John Allen